
- Running mac os in the cloud how to#
- Running mac os in the cloud for mac#
- Running mac os in the cloud mac os x#
- Running mac os in the cloud install#
- Running mac os in the cloud generator#
Runners use a shell to execute the step scripts, and the host machine will be shared by multiple steps that are scheduled to execute on the runner. Be sure to check for any memory issues due to this limitation. This is may occur when sometimes there will be enough swap memory available and a build may pass, while other times not enough swap is available, which could cause the same build run out-of-memory. This may result in non-representative build results about memory usage and out-of-memory (OOM) errors. It is not possible to completely disable swap memory so processes created by steps that are run on the runner will likely use swap memory. Limitations for MacOS Runner Memory used by the Runner It is your responsibility to make sure the scripts you run in each step won’t have a major impact on other steps. To compensate for this, the runner try to empty the build directory empty after each step. Any side effects generated by the step (such as, installing any applications, starting a database service, or editing a file outside of the build directory) would potentially affect the next step to be run (including new pipeline runs). This allows the runner to execute applications on the host, but does not provide a clean build environment for every step. MacOS Runners use Bash to run pipeline steps on your MacOS machine (host device). Open Terminal (or shell of your choice), go to the bin directory under your Runner folder, run the command provided in Run step on the Runner installation dialog. Untar the file to the desired directory, for example: /Users/your_user_name/atlassian_runner It is a solid, well-known SSH client that is quite popular.Currently we only support running one runner per machine.įor Workspace runners, visit Workspace settings > Workspace runners.įor Repository runners, visit Repository settings > Runners.įrom the Runner installation dialog, under System and architecture, select MacOS (x86 / Apple Silicon).ĭownload the tar.gz file provided in the Run step on the Runner installation dialog.
Running mac os in the cloud install#
Once you have MacPorts installed, you just need to give this command: sudo port install puttyĪnd to add a shortcut on the Desktop, cp /opt/local/bin/putty ~/Desktop/PuTTY Alternatives to PuTTY on the MacĪ lot of people use Cyberduck on Mac.
Running mac os in the cloud how to#
To see how to install MacPorts and PuTTY, see here. If you already have the brew command installed, the best way to install PuTTY is to use the following command: brew install putty Installation using MacPorts
Running mac os in the cloud for mac#
You can now use the key for logins from scripts and command line with: ssh -i privatekey.pem Ported PuTTY for Mac It should only be readable by the user that owns it.
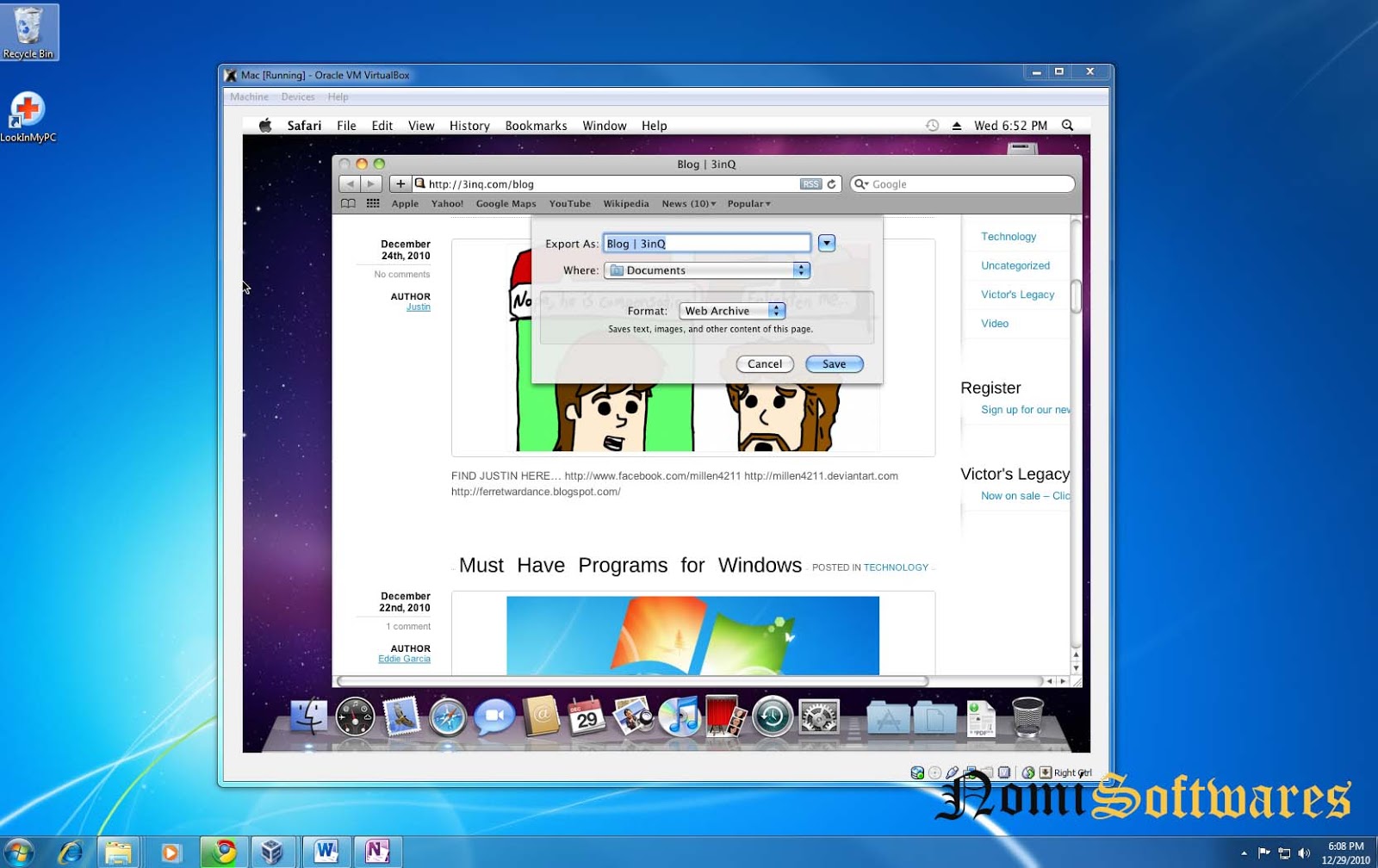
Make sure permissions on the private key file are set properly. ppk format private key to a standard PEM format private key: puttygen privatekey.ppk -O private-openssh -o privatekey.pem

Then, use the following command to convert the.
Running mac os in the cloud generator#
This will also install the command-line version of puttygen, the PuTTY key generator tool.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/amazon-music-sign-in-5bd33a4f46e0fb00513c2215.png)
ppk format private key and want to use it with the built-in OpenSSH on Mac on the command line or in scripts, you can use the following commands.įirst, install PuTTY for Mac using brew install putty or port install putty (see below). How to use PuTTY SSH keys with the built-in OpenSSH This is recommended for users who are not accustomed to using a command line. This opens a graphical dialog asking for the host to connect to and the user name. The second option is to select New Remote Connection. Running SSH with a graphical user interface This is more familiar for Linux and Unix users who are used to using a command line. The first approach is to type ssh hostname or ssh into the terminal window. Once you have the terminal window open, you have two alternatives. Running SSH from the terminal command line Terminal can be used to get a local terminal window, and also supports SSH connections to remote servers. To use it, goto Finder, and selext Go -> Utilities from the top menu.
Running mac os in the cloud mac os x#
Mac OS X includes a command-line SSH client as part of the operating system. Contents Using the built-in SSH client in Mac OS X Running SSH from the terminal command line Running SSH with a graphical user interface How to use PuTTY SSH keys with the built-in OpenSSH Ported PuTTY for Mac Installation using HomeBrew Installation using MacPorts Alternatives to PuTTY on the Mac Using the built-in SSH client in Mac OS X


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
